Critical Care
Key Points
Although the majority of people with COVID-19 have uncomplicated or mild illness (81%), some will develop severe illness requiring oxygen therapy (14%) and approximately 5% will require intensive care unit treatment. Of those critically ill, most will require mechanical ventilation.
The most common diagnosis in severe COVID-19 patients is severe pneumonia, defined as fever or suspected respiratory infection, plus one of the following: respiratory rate > 30 breaths/min; severe respiratory distress; or SpO2 ≤ 93% on room air.
Management of COVID-19 critically ill patients involves best practice treatment for viral pneumonia and ARDS.
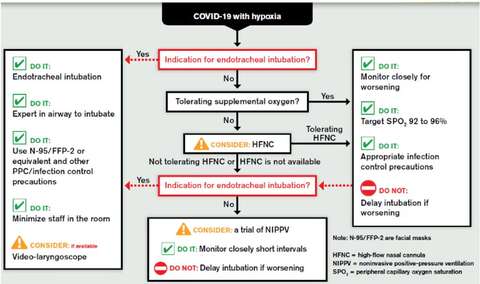
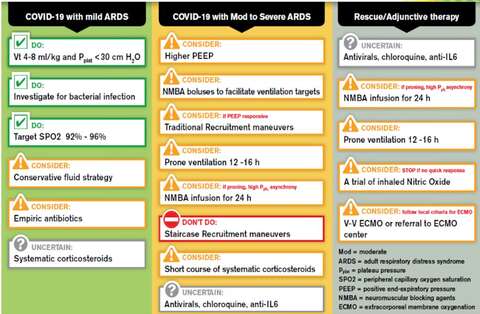
Source: Society of Critical Care Medicine and European Society of Intensive Care Medicine
VENTILATION
Non Invasive Ventilation
- Given the aerosol generating risk, use NIPPV with caution and appropriate isolation for CPAP/BIPAP/high-flow nasal cannula.
- In patients treated with CPAP or NIPPV, attention should be paid to those presenting with clinical signs of excessive inspiratory efforts, where intubation should be prioritized to avoid excessive intrathoracic negative pressures and self-inflicted lung injury. (https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1164/rccm.202003-0817LE)
Invasive ventilation - Lung Protective Ventilation Strategies
- Consider early invasive mechanical ventilation with lung protective ventilation
- Tidal volume - 4 - 8 ml/kg of predicted body weight
- Pplateau < 30 cm H2O
- For moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (PaO2/FiO2 < 150)
- Consider neuromuscular blocking agents
- Consider prone positioning +/- ECMO
note: enteral feeding is not contraindicated in prone positioning
- Consider neuromuscular blocking agents
- Proper conduct of prone positioning VIDEO
Advise against the ventilation of multiple patients on a single ventilator
- Tidal volumes disproportionately delivered to the most compliant lungs
- Impossible to monitor pulmonary mechanics or individualize PEEP
- Patients may progress at different rates becoming more dissimilar in their mechanics
Onset: within 1 week of a known clinical insult or new or worsening respiratory symptoms.
Chest imaging (radiograph, CT scan, or lung ultrasound): bilateral opacities, not fully explained by volume overload, lobar or lung collapse, or nodules.
Origin of pulmonary infiltrates: respiratory failure not fully explained by cardiac failure or fluid overload. Need objective assessment (e.g. echocardiography) to exclude hydrostatic cause of infiltrates/oedema if no risk factor present.
Oxygenation impairment in adults :
- Mild ARDS: 200 mmHg < PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 300 mmHg (with PEEP or CPAP ≥ 5 cmH2O)
- Moderate ARDS: 100 mmHg < PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 200 mmHg (with PEEP ≥ 5 cmH2O)
- Severe ARDS: PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 100 mmHg (with PEEP ≥ 5 cmH2O)
• When PaO2 is not available, SpO2/FiO2 ≤ 315 suggests ARDS (including in non-ventilated patients) (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193(1):52-9)
FLUID MANAGEMENT & VASOPRESSOR SUPPORT
Fluid Management
- Conservative fluid strategies are recommended.
- If fluid resuscitation is needed, use balanced crystalloids (e. g., Plasmalyte or Lactated Ringer’s).
Vasopressor Support
- If vasopressor support is needed, suggest use norepinephrine as the first line. Add vasopressin if a 2nd vasopressor is required.
- consider dobutamine if there is evidence of cardiac dysfunction
INFECTION TREATMENT
 |  |
- Collect specimens from the upper respiratory tract (URT) AND, where clinical suspicion remains and URT specimens are negative, collect specimens from the lower respiratory tract when readily available for COVID19 virus testing by RT-PCR
- Test and treat co-existing bacterial infections (see SHS_UHN Antimicrobial stewardship website for up-to-date information COVID - 19 | SHS+UHN ASP)
- No conclusive evidence for antiviral or immunomodulation therapies - no role at present outside proper research trials
VENTILATORS
GE Healthcare
SpringerNature
Drager
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
Click HERE for additional resources